self-service analytics
What is self-service analytics?
Self-service analytics is a type of business intelligence (BI) that enables business users to access, manipulate, analyze and visualize data, as well as generate reports based on their discoveries. By working directly with the data, users can gain quick insights into the information, identify potential business opportunities and make data-driven business decisions, without needing a background in statistics, data science or other areas of technology.
Self-service analytics requires a front-end BI application (on-premises or online) with a user-friendly interface that enables users to easily view and manipulate the data. To this end, many vendors offer products or services that let users work directly with data that comes from multiple sources. Popular examples of such products include Tableau, ThoughtSpot and Microsoft Power BI.
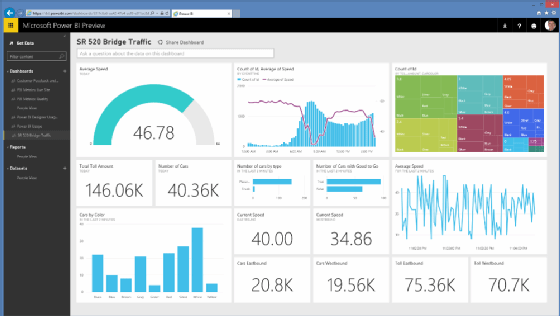
A front-end BI application provides users with an interface for easily working with the data to get at the results they need. Users can also create dashboards that include graphs, tables, key performance indicators (KPIs) and other elements that help to understand the data. Often these elements let users drill into the data so they can easily access related data or data at a different granularity. A BI application also lets users generate reports in different formats, which can then be shared with other stakeholders.
However, self-service analytics is more than just a front-end application. It is an entire process that might require the data to be collected from multiple sources and transformed into a clean, accurate and complete data set -- a process that might be referred to as extract, load and transform (ELT). If the user needs the BI application to interface with multiple data sources, each of those data sources must have clean and reliable data.
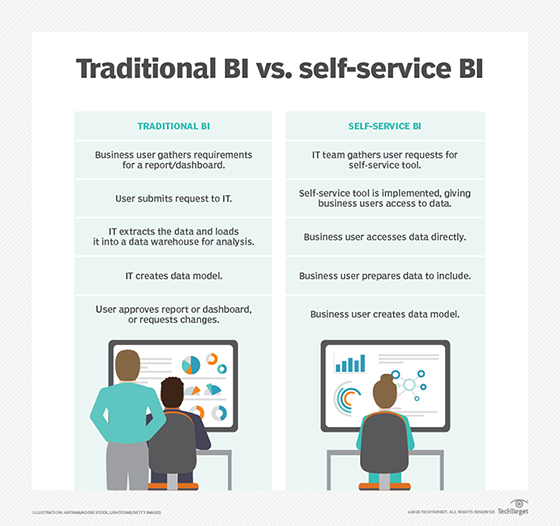
In addition, the data must be fully protected to address both security and privacy concerns, wherever it resides, and it must be readily available to users when they need to work with it. Establishing and maintaining the source data is often the most complex and resource-intensive part of a self-service operation. That said, if the data is already in pristine shape, then connecting to that data is usually a straightforward process.

What are the business benefits of self-service analytics?
In the past, data analytics was solely the domain of trained data analysts and data scientists, usually with support from IT. However, many organizations have implemented self-service analytics systems or plan to implement them because they offer several important benefits:
- Increased efficiency. Business users can access the data they need when they need it and work with the data in a way that best fits their circumstances. They do not have to wait for a data analyst or other team member to respond to their requests for specific information. With self-service analytics, business users have immediate access to relevant data that they can use to create dashboards and generate reports.
- Faster decision-making. Business users can make decisions more quickly because they have immediate access to the data they need and the capability to analyze and visualize that data on an ad hoc basis. As a result, they can respond to changing trends, new opportunities or critical developments much faster than they would if relying only on traditional approaches to BI.
- Greater collaboration. Self-service analytics enables business users to collaborate more easily about data-related issues. Everyone is working with the same data, so they have a common reference point for their discussions. They can also easily share their data-driven insights with each other, backing up those insights with comprehensive visualizations and reports. In this way, self-service analytics can help facilitate clearer and more effective communication.
- Better use of time. IT teams and data teams can have a difficult time keeping up with the data-related requests that often come with a traditional BI system. Self-service analytics can help eliminate many of these requests, freeing up IT and data teams to focus on other priorities and initiatives.
Critics of self-service analytics maintain that only a trained data scientist or other professional can reliably understand the meaning of certain data correlations. If the analysis is not carried out correctly or the data is misinterpreted, those relying on the analysis might make poor decisions that could potentially damage the organization.
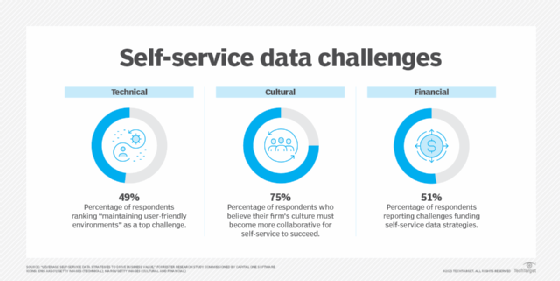
To avoid such scenarios, business users should receive the training and support they need to use self-service analytics effectively. At the same time, the data and IT teams should have in place a comprehensive data governance policy that ensures the data is being properly managed and protected at all times.
Read expert advice on how to start with self-service analytics and explore 10 dos and don'ts for deploying self-service BI tools. Learn about the different types of business intelligence tools and key features to examine and more about self-service business intelligence.






